What is gum recession?
Receding gums are an insidious problem that many of us are unaware of when they occur, but over time, they can pose a serious threat to our oral health. Medically known as periodontitis, this condition actually begins with the gums gradually pulling away from the teeth. While it may initially appear as minor sensitivity or a slight bleeding while brushing, over time, the roots of the teeth become exposed, teeth become loose, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss.
Many people believe that receding gums are simply a natural consequence of aging, but this is a completely false belief. Receding gums can occur at any age. Factors such as genetic predisposition, poor brushing habits, tartar, smoking, or teeth grinding (bruxism) contribute to this condition. Even a toothbrush with very hard bristles can damage the gums and accelerate the process.
The most dangerous aspect of receding gums is that they usually progress painlessly. So, while your gums may be receding without you even realizing it, you might still feel like everything is fine. However, if you notice your teeth appear longer when you look in the mirror, this could be a silent sign of receding gums.
The good news is that when detected early, receding gums can be stopped and, in some cases, even reversed with treatment. Regular dental checkups, proper oral hygiene habits, and a healthy lifestyle are crucial for this.
What is Receding Gums?
Gum recession, as the name suggests, is a condition in which the gums gradually recede from the teeth. This means that the pink protective tissue that tightly surrounds the teeth gradually recedes over time, exposing the roots. Normally, our gums protect our teeth like a shield from external factors and bacteria. However, when this shield weakens, the roots of our teeth become vulnerable, and problems begin.

This condition isn’t just an aesthetic problem; when the tooth root is exposed, it can lead to serious consequences, including sensitivity to hot and cold, pain, decay, and even tooth loss. In short, gum recession is a seemingly minor condition that can radically impact our oral health if left untreated.
Many people experiencing gum recession don’t initially notice it. It’s usually painless. However, over time, symptoms such as longer teeth, bleeding during brushing, or sensitivity begin to appear. Therefore, even if you notice a slight change in your gums, don’t assume it will “just go away.” Taking precautions early is the most effective way to protect both your gums and your smile.
Causes of Receding Gums
Gum recession is a problem that usually progresses slowly, but is often quite advanced by the time it’s noticed. While many people think, “I woke up one morning and my gums were receding,” this process actually develops over months or even years. So why do gums recede, and what’s behind this process?
Inadequate or Improper Oral Care
Neglecting oral care is one of the most common causes of receding gums. Failure to brush regularly, floss, or remove tartar can lead to inflammation in the gums. This inflammation eventually leads to the weakening and recession of the gums. Brushing your teeth is certainly important, but using the right technique is just as important.
Brushing Too Hard
Some people think, “The harder I brush, the cleaner it will be,” but this is one of the biggest misconceptions about gums. Hard-bristled brushes or brushing with excessive pressure damage tooth enamel and irritate the gums. In the long run, this can lead to receding gums. So, the key to cleaning is gentleness, not strength.
Genetic Predisposition
Unfortunately, sometimes, no matter how careful you are, genetic factors can come into play. If someone in your family has gum disease, your risk of developing it increases. In this case, regular dental checkups are the most effective way to manage your genetic risk.
Smoking
Smoking is one of the biggest threats to your gums. This is because smoking reduces blood flow to the gum tissue and slows down the healing process. It also increases the buildup of plaque and tartar on the tooth surface, accelerating gum recession. Quitting smoking is one of the best steps you can take not only for your gums but also for your overall health.
Clenching and Grinding Teeth (Bruxism)
Some people unconsciously clench or grind their teeth at night. This habit puts constant pressure on the gums, causing them to recede over time. If you wake up with a sore jaw or notice wear on your teeth, bruxism may be the underlying cause.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes in women during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause make the gums more sensitive. During these periods, the gums are more susceptible to inflammation and recession. Therefore, extra attention to oral hygiene is necessary during these times.
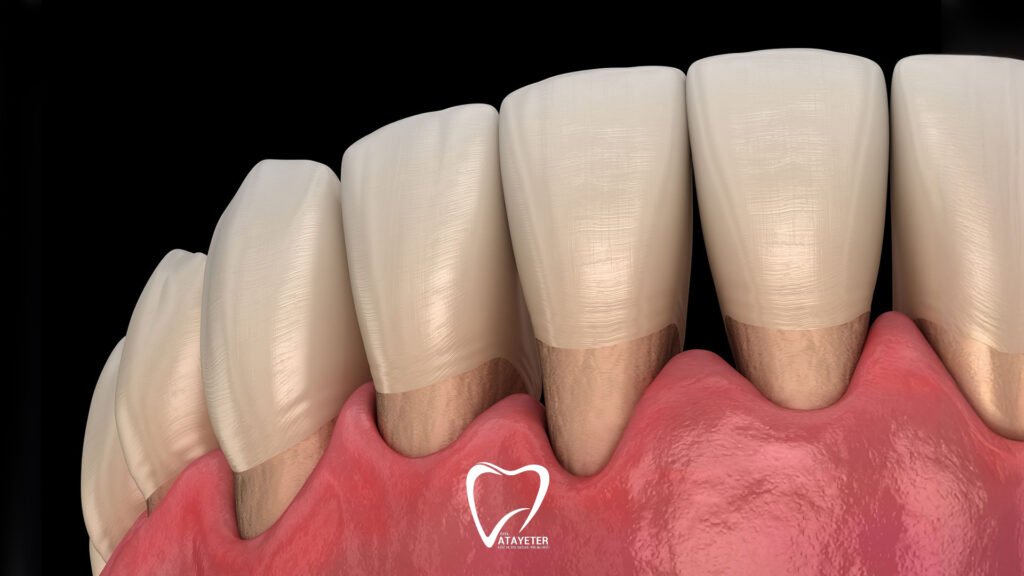
Receding gums are often a silent problem that can be difficult to detect, but their consequences can be serious. Many people don’t even realize it until symptoms appear. However, if you’re attentive, you can pick up on some subtle signals your body is sending you. Here are the most common symptoms of receding gums:
Tooth sensitivity:
If you feel a sudden sting in your teeth when you drink hot coffee or rinse your mouth with cold water, this could be one of the first signs of receding gums. This sensitivity increases, especially as the roots of your teeth begin to become exposed.
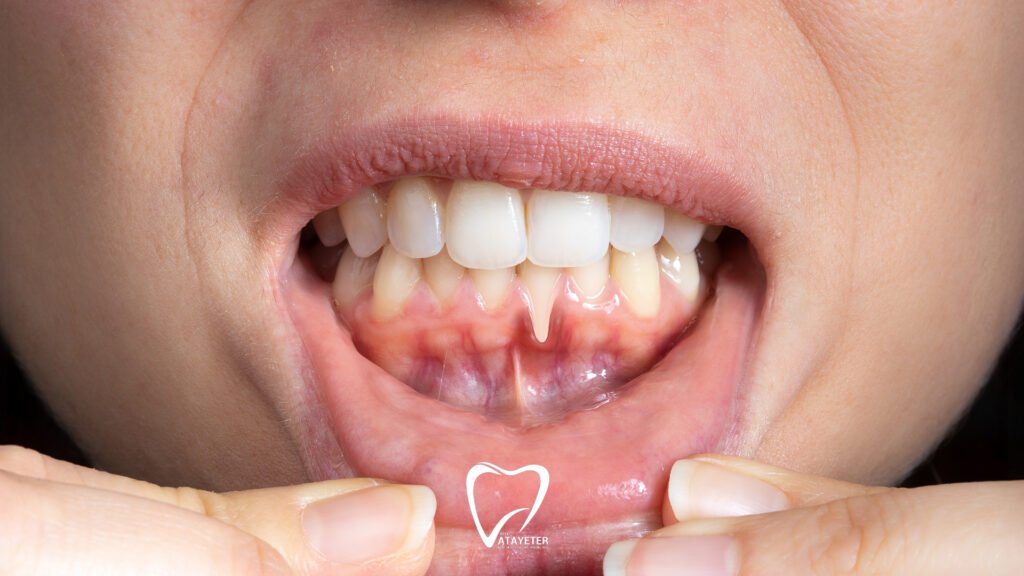
Redness and swelling of the gums:
Healthy gums are pale pink. If your gums are red, swollen, or tender, it indicates an infection in the area.
Bleeding when brushing or flossing:
If you experience bleeding while brushing or flossing, don’t dismiss it as “normal.” This is one of the clearest signs that your gums are not healthy.
Teeth Appear Longer:
If you notice your teeth appear longer than before when you look in the mirror, this is a clear sign of gum recession. As the gums recede, a portion of the tooth root is exposed, making the tooth appear longer than it actually is.
A Feeling of Loose Teeth:
In more advanced cases, a slight movement may be felt in the teeth as the bone and tissue supporting the teeth weaken. This indicates that gum recession has reached a severe stage.
Bad Breath (Halitosis):
Gum disease, along with the proliferation of bacteria, can cause bad breath. If bad breath persists despite regular brushing, gum recession may be the underlying cause.
How to Diagnose Receding Gum
Diagnosing receding gums is actually quite simple, yet crucial. While often unnoticed, a dental examination can easily reveal the condition. During the examination, the dentist carefully examines the connection between the gums and the teeth, measures the depth of any gum pockets, and assesses for any signs of inflammation.
In some cases, a visual examination alone is not sufficient. In such cases, the dentist may request an X-ray to visualize the bone structure beneath the gums. This is because receding gums can affect not only the gums but also the bone tissue that supports the teeth. If bone loss is present, this indicates that the disease is progressing, and a treatment plan is tailored accordingly.
In short, while gum recession is often subtle, all the details become clear during a dental exam. Therefore, if you notice even the slightest changes in your gums, it’s best to see a specialist immediately. Early diagnosis is key to protecting both your gums and your teeth.
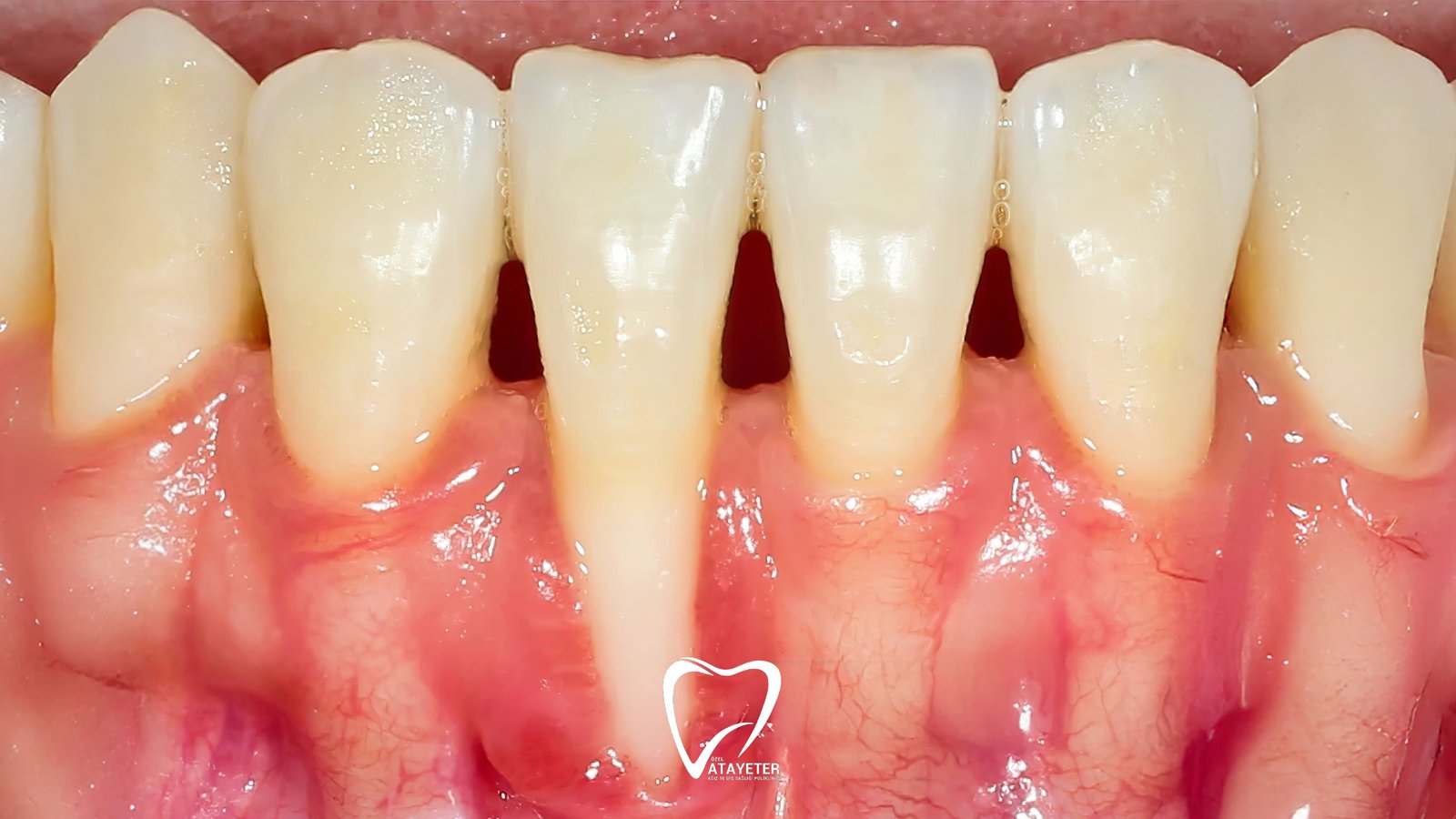
Receding Gum Treatment
Treatment for receding gums varies depending on how advanced the problem is and the underlying cause. While it can be stopped with fairly simple methods when detected early, more extensive treatments may be necessary in more advanced stages. The key is to recognize the process early and take the right action.
If receding gums are still in their early stages, professional cleanings recommended by your dentist can restore gum health. Scaling involves carefully removing plaque and tartar from beneath the gums using specialized tools. These deposits are a major cause of gingivitis. After the cleaning, the gums relax, blood circulation increases, and the tissue begins to repair itself.
The next step is root planing. This treatment smooths the tooth root surfaces, making it more difficult for bacteria to reattach, and allows the gum to reattach firmly to the tooth surface. This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and is painless.
If gum recession is advanced, cleaning alone may not be sufficient. In this case, surgical intervention is considered. In cases where gum tissue has been severely lost, procedures called “gum grafting” are performed. Healthy tissue taken from the mouth is transplanted to the recessed area, protecting the root of the tooth. This procedure both improves the aesthetic appearance and reduces tooth sensitivity.
In recent years, some clinics have also opted for laser technology in gum treatment. Laser treatments reduce bleeding and accelerate the healing process. Furthermore, because this method is virtually painless, many patients consider it a more comfortable option.
After treatment is completed, regular oral care is crucial to prevent gum recession from recurring. It’s crucial to learn proper brushing techniques, use dental floss or interdental brushes, and maintain regular dental checkups. Remember, once gum recession has begun, it’s impossible to completely ignore it, but with the right treatment, it’s always possible to stop it and restore healthy gums.






Comments are closed